Flipped classrooms are a blended learning style where students engage in their own learning pre class at home and then come together during class time to apply what they’ve learned and deepen their understanding of the course material in an interactive and creative way.
It’s the reverse, or “flip,” of a traditional learning environment, where students are taught course materials in class in the form of a lecture or lesson and then asked to apply the information they’ve learned through homework assignments at home.
Khan Academy is a great example of an organization that uses the flipped classroom model to teach children math. And while a flipped classroom model is often used in traditional academic settings, course creators can apply the flipped classroom model to their online courses too.
In this article, we’ll help you better understand the flipped classroom approach , its pros and cons and how to apply it in your classroom or online course.
Understanding the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom combines synchronous and asynchronous learning incorporating individualized learning activities and face to face interactions.
During the individualized learning stage, students watch videos and read course materials at home at their own pace. Then, they can interact with the course materials as often as they want before coming together in class.
In class, students participate in organized class activities to deepen their understanding of the course material. It’s the reverse of a traditional classroom, where class time involves learning the course materials, and the application takes place at home.
For example, think of a university classroom where a teacher holds a traditional lecture and then asks students to apply the course lessons through papers and assignments.
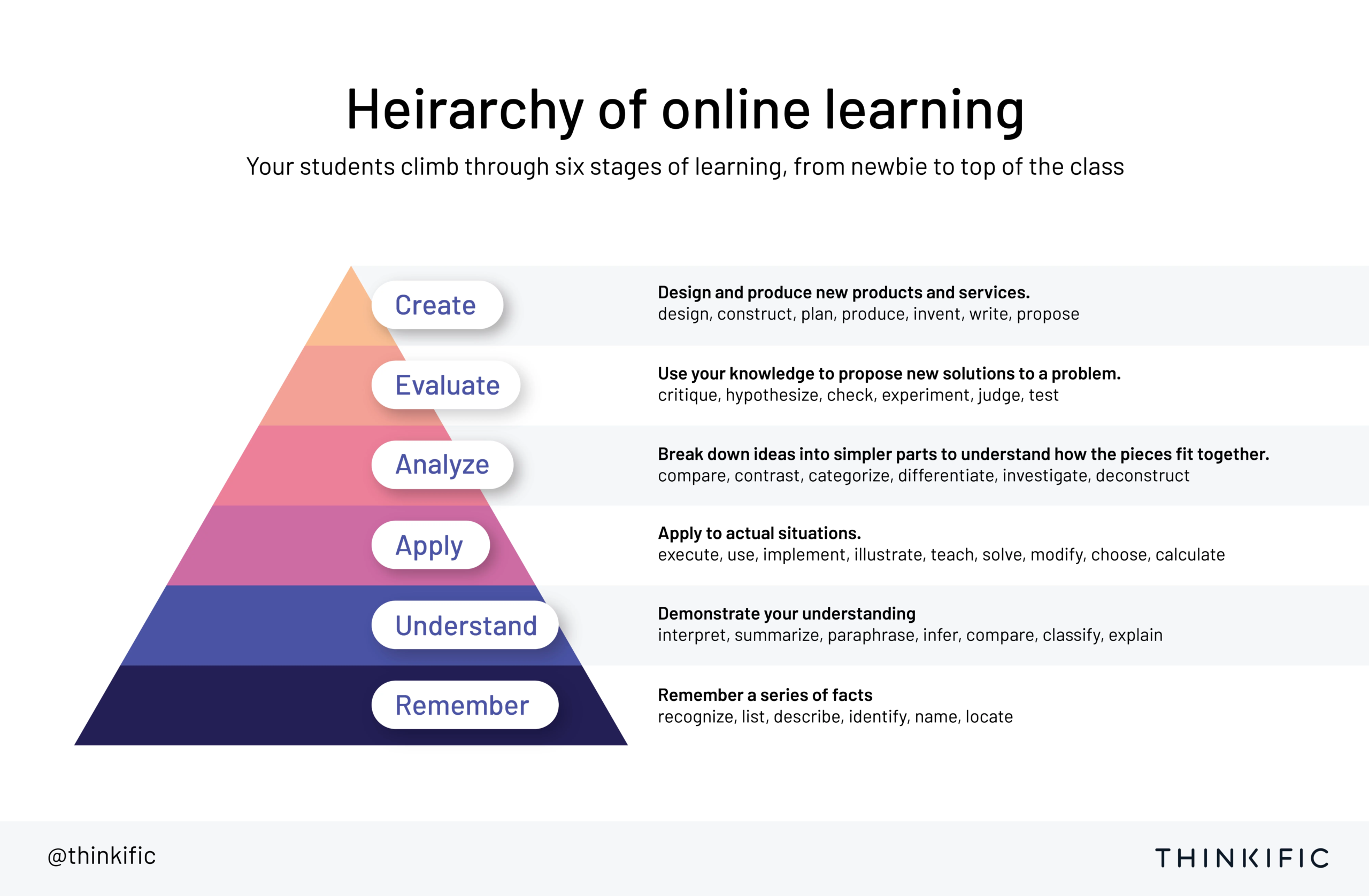
Bloom’s Taxonomy highlights the concept of how traditional classrooms have functioned. Traditionally, lower level learning, such as understanding and remembering, occurs in the classroom.
The flipped classroom is modeled around the concept that having students sit through lectures is not the best use of time. So instead, class time is reserved for higher level learning on the pyramid like the analyze and apply stage.
Let’s look at an example. Imagine a math class. Using the flipped classroom model, a teacher would assign students a video about a math concept. Class preparation would involve students watching the video ahead of class. Then, in the classroom, students would spend their time problem solving by participating in math-based class activities designed to practice and analyze the concept.
The History of the Flipped Classroom
The flipped class was first introduced as a concept by Jonathan Bergman and Aaron Sams in 2007 when they began recording their classroom lectures. Technology made it easy to share these videos with their students. Bergman and Sams observed that student understanding deepened when students watched lessons ahead of time, freeing up time to apply their learning in class.
The pair noticed that with a teacher available to answer questions, students’ broadened their understanding of the course materials better than ever before. They went on to write a book called FlipYour Classroom: Reach Every Student in Every Classroom Every Day. Since then, many classrooms around the world have adopted the flip model.
Advantages of a flipped classroom
There are many advantages of a flipped classroom. One is that it allows students to work on gaps of misunderstanding with the help of a teacher. Another is that it enables students to use class time to apply their learning rather than constantly being introduced to new material in class.
A flipped classroom is also flexible. Students can learn at their own pace and return to the videos and materials as often as they need. In addition, no time is wasted translating and transcribing information from a textbook.
With the flipped classroom model, students are responsible for their learning which is empowering. Individual students decide how much they want to get out of the course materials and concepts.
Finally, a flipped classroom allows for more interaction and learning between teachers, students and classmates. There are endless opportunities for problem-solving, with a teacher nearby to help, as well as opportunities for collaboration between students.
Disadvantages of a flipped classroom
Despite the many advantages of the flipped classroom, there are always two sides to a coin. Many have criticized the model’s reliance on increased screen use and access to technology that some families don’t have.
Another criticism is that the model reduces self-directed critical thinking that happens when working on assignments alone. Still, it’s easy to see that the advantages of a flipped classroom far outweigh the disadvantages.
The four pillars of flipped learning
The four pillars of a flipped learning are; flexible environment, learning culture, intentional content, and professional educator. We briefly summarize all four below.
Flexible environment
In the flipped classroom, students have lots of autonomy to choose what they want to learn and when. Educators are also encouraged to be flexible with their expectations on timelines and assessment of their students’ learning.
Learning culture
In traditional classrooms, teachers are the primary source of information. Flipped learning shifts this model to a learner-centered approach. Teachers spend their school time using active learning strategies to create learning opportunities and help students explore topics in greater depth.
Intentional content
The flipped classroom model aims to understand how educators can use the flipped model to help students develop conceptual understanding. The teacher determines what they need to teach and what materials and content students should explore independently.
Professional educator
In a flipped class, the professional educator takes a more hands-on approach than in a traditional classroom. Educators are encouraged to be open to constructive criticism and continually reflect on and adjust their teachings.
The flipped classroom and your online course
Now that you understand how a flipped class works, you can begin to apply it to your very own online course. After all, the principles behind the flip classroom are ideal for teaching online. Consider creating evergreen video and hosting a course where your students join specific live sessions on zoom.
Take it a step further by dividing people into breakout rooms to apply their knowledge and utilize a Facebook page to allow participants more opportunities to collaborate and interact with you.
Thinkific is the ideal platform to create your next course.
Try Thinkific for free and get the course creation, marketing, and selling tools you need to turn your ideas into a rocking and interactive online course. (No technical skills required!)





