Even though every instructor is unique, the prevalent style of teaching has changed dramatically over the past 50 years, along with the new cultural norms and technological advancements.
Educational researchers today define at least five different teaching styles on a spectrum that moves from a teacher-centered approach to a student-centered one:
Other teaching methods outside of the core five exist as well. The Spectrum of Teaching Styles in Physical Education defines 11 distinct teaching styles that can be used to coach students in schools and universities.
While most instructors can be described by a single personal model of teaching, the best ones always adjust their teaching strategies to their students and the learning process at hand.
That’s why it’s important to know what the different teaching styles are and have a clear idea of how to use them when needed.
Skip ahead:
- 5 different teaching styles to use today
- Is one style of teaching better than others?
- How to adapt teaching styles to different learning styles?
- Does classroom diversity influence my style of teaching?
5 different teaching styles to use today
A lot of educators in traditional teaching environments with decades of experience are not aware of their primary teaching style, even though their approach to teaching has a direct effect on student participation and student engagement.
Let’s explore five teaching style examples to show how broad differentiated instruction in classroom settings can be.
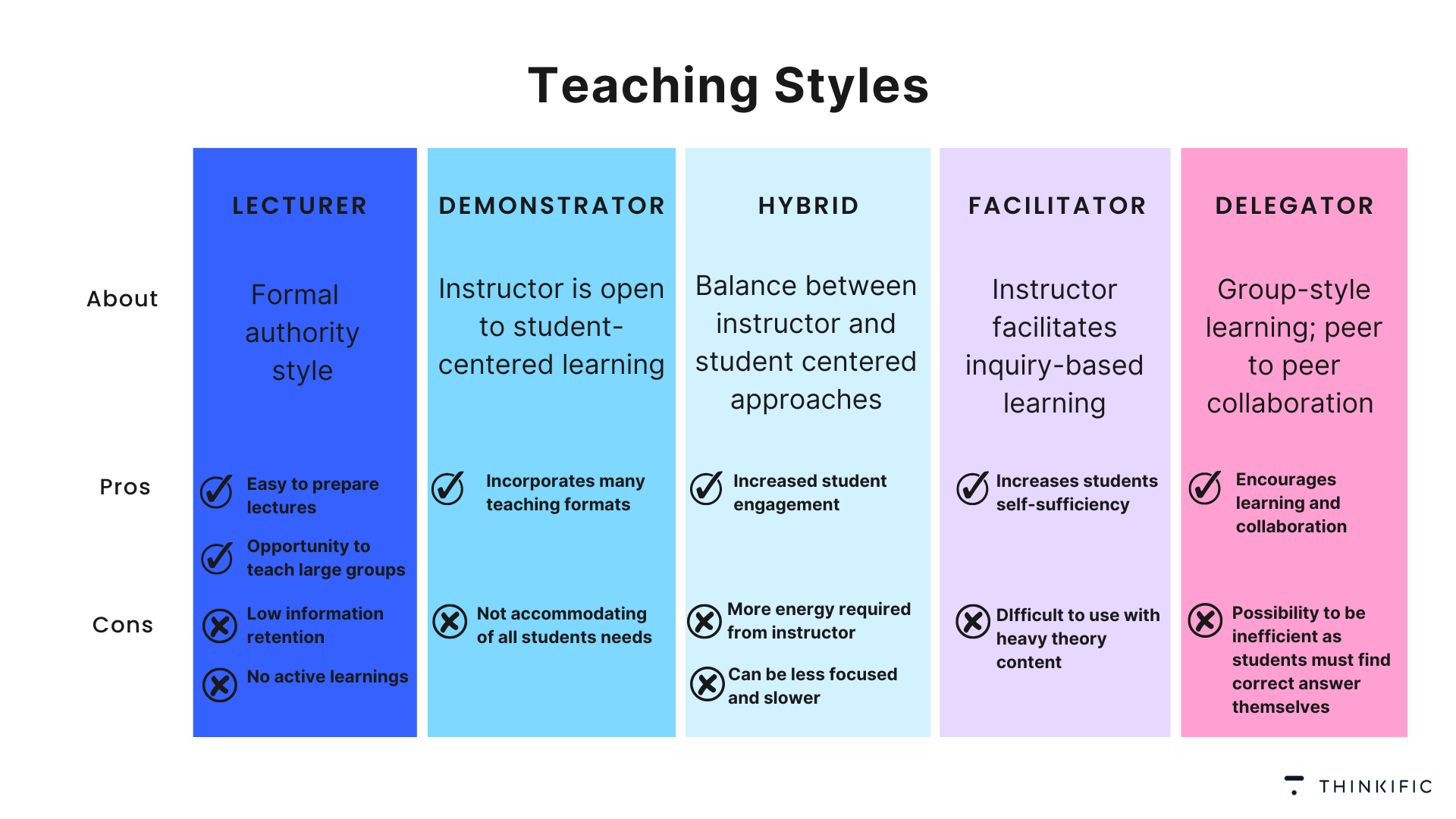
The lecturer style (sometimes called the formal authority style) is familiar to anyone who’s sat through long unidirectional lectures in giant university auditoriums. In this teaching style, the teacher takes up a central role and delivers information to a large group of students in a structured and organized manner. The subject matter is usually singular and predetermined.
Because the students are many, there’s not enough room or time for personalized interactions between the teacher and the students. However, students are encouraged to take notes and ask questions at the end of each lecture. There are usually no activities planned.
An example of the Lecturer teaching style in action is when a guest speaker is invited to a school or an office to give a presentation. After the guest speaker presents the topic for an hour, they encourage students to ask questions if there’s anything they don’t understand or would like to clarify.
Pros of the Lecturer teaching style
- It’s possible to teach large groups of students at once
- It’s easy to prepare lecturers
- It provides a clear structure and organization to the content
- It can be time-effective in covering a broad range of material
Cons of the Lecturer teaching style
- There’s limited student engagement and interaction
- Students won’t be able to retain information properly because they’re not actively engaging with the lecturer
- This teaching method does not cater to diverse learning styles
Under the demonstrator style, the teacher still retains a lot of authority but is more open to trying a student-centered approach to teaching. You can see the demonstrator encouraging students to come up with problem-solving strategies, ask questions and simulate what they’ve just learned.
The demonstrator often goes beyond lectures and demonstrates concepts or skills to the students using visual aids (presentations, images, and films), hands-on activities, and practical examples. As a result, this method is applicable to more learning styles.
An example of the Demonstrator teaching style in action is when a teacher conducts a science experiment or an art workshop in the classroom. The students huddle around the demonstrator to observe and participate in the experiment or workshop. When the teacher is done with the demonstration, they encourage the students to emulate the processes that they’ve observed to create the same (or similar results).
As the students work, the teacher is there to provide them with visual aids and multimedia to enforce concepts and principles, and answer any questions they may have regarding the project. The teacher may also encourage peer sharing and feedback, which helps students to actively engage in the learning process.
Pros of the Demonstrator teaching style
- It incorporates a variety of teaching formats
- Hands-on learning can enhance students’ understanding of the subject matter
- Visual aids and demonstrations can make concepts more memorable
- Students can ask for immediate clarification through examples and practical applications
Cons of the Demonstrator teaching style
- It doesn’t accommodate the needs of all students
- This teaching style may not be suitable for all subjects or topics
- This style requires adequate resources and preparation, which can be hard if the teacher is short on time or has a low budget
- During a demonstration, there’s often no time to cover a large amount of content
The hybrid (also known as blended) style strives to strike a balance between teacher- and student-centered approaches. It also tries to integrate both traditional and modern teaching methods, which makes it a great style for adapting to the needs of diverse learners.
Most of the time, the teachers who follow the hybrid style bring their own knowledge and expertise into the class. They still have a structure for every lecture but are able to adjust their flow and come up with the right activities to keep the students engaged. A hybrid teaching style integrates lectures, demonstrations, group activities, and even technology into one learning session.
For example, a hybrid teacher may assign online readings or videos for students to review before class. There can also be an online discussion forum where students share insights and questions. In class, the students can build upon the online discussion with hands-on activities, group discussions, or problem-solving tasks related to the material they reviewed.
While the hybrid approach tends to be quite effective in a variety of settings, it can make covering information-heavy courses difficult due to its slower pace.
Pros of the Hybrid teaching style
- This teaching style uses a variety of methods that cater to diverse student needs
- It integrates traditional and modern approaches for a balanced learning experience
- It gives teachers the flexibility to adapt to different learning preferences
- Students remain active and engaged for longer
Cons of the Hybrid teaching style
- This teaching style requires careful planning and the coordination of different teaching elements
- Finding the right balance between traditional and modern teaching methods may be challenging
- It’s dependent on the available resources and technology
- It can be less focused and slow
- It requires a lot of energy from the teacher
Shifting to an even more student-centered approach, there’s the facilitator style of teaching.
Instead of giving one-directional lectures, a facilitator encourages inquiry-based learning. Students learn by thinking critically, asking questions, and discussing real-world case studies. Some other activities might be designed to improve problem-solving skills and help understand the subject matter better through practical challenges.
A great example of the Facilitator teaching style in action is a Socratic seminar, which promotes Socrates’ belief that asking questions, inquiring about things, and engaging in constructive debates are the best ways to learn.
In a Socratic seminar, students seek a deeper understanding of complex or vague ideas through thoughtful dialogue and divergent thinking. The facilitator provides a specific topic or text for students to read through and ponder upon. Then, the facilitator poses open-ended questions to stimulate critical thinking. The students answer these questions, argue civilly for or against a motion, share ideas, and build on each other’s responses to get an all-around understanding of the topic/text.
Another example is a case study analysis, where the facilitator presents a real-life case study related to the subject matter. Then, the facilitator prompts a class discussion where students analyze the case, identify key issues, and proffer solutions. The teacher guides the discussion, encouraging critical thinking and collaboration among students.
Pros of the Facilitator teaching style
- This teaching style helps students develop self-sufficiency, as the teacher provides guidance and support rather than direct instruction
- It fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and communication skills
- It supports student-centered learning and autonomy
Cons of the Facilitator teaching style
- This style doesn’t work well for theory-heavy classes
- It requires a skilled facilitator to guide discussions effectively
- It may take more time to cover content compared to traditional methods
- Students may need additional support if they’re not accustomed to this teaching method
The most student-centric teaching style of all is called the delegator style (also known as the group style). Here, the teacher is merely present as an observer, and it’s the group of students who are doing all the work.
Most of the learning in the delegator style happens peer-to-peer, through frequent collaborations and discussions. The instructor is practically removed from the position of authority and only facilitates the discussions instead.
The delegator style works best for lab-based experiments, group tutoring classes, creative writing, debates, and other peer-to-peer activities. In these activities, the teacher divides the class into small groups and assigns each group a project related to the course content. The students are responsible for planning, executing, and presenting their findings, while the teacher acts as a mentor, providing guidance and support throughout the project.
This approach encourages students to take ownership of their education and become self-directed learners.
Pros of the Delegator teaching style
- This teaching style encourages learning and collaboration among students
- It allows for individualized learning experiences
- It promotes the development of problem-solving and decision-making skills
Cons of the Delegator teaching style
- This teaching style can be inefficient since students have to find the right answers for themselves
- It may not be suitable for all subjects or students
These are just five of the most popular teaching styles that instructors can choose from when creating their courses. Depending on the system you look at, there might be even more, as described in a paper titled Teaching Styles and Language Performance by Edgar R. Eslit and Mercedita B. Tongson.
Is one style of teaching better than others?
As you can see from the list above, each style of teaching has its pros and cons. So there’s no definitive winner here — rather, you should learn to mix and match based on a situation.
When preparing your course content, you can imagine which teaching style would help your students learn the material best. If you’re not sure, try experimenting with a few different styles for the first few student cohorts to find out.
How to adapt teaching styles to different learning styles?
We’ve written about the seven main types of learning styles before, which are essential for every instructor to understand.
There’s no doubt that different students shine under different teaching approaches.
There’s a famous “empty vessel” theory, for example, which asserts that students’ minds are essentially empty until teachers pour their knowledge into them, lecture-style.
But cooperative learning which requires more group work and would pair well with the facilitator or delegator style of teaching. Check out Cohort-Based Learning for a deeper dive into this kind of teaching style.
Interactive learning can be a great fit for the demonstrator or facilitator style, and so on.
Does classroom diversity influence my style of teaching?
Another reason to have different teaching styles in your arsenal is the diversity of students you might see in your class. As students learn better by different approaches and at a different speed, you should be able to adjust your teaching style on the fly to maximize the learning opportunity for all.
It’s likely that your primary teaching style won’t be purely of the big five discussed above, but rather an ever-changing mix that would be unique to you and the students you teach.
In addition, as teachers lead students and help students become future leaders, you should be aware of the kind of leadership that you want to facilitate through your teaching.
How to create a perfect course online
Do you want to put your teaching style to practice? There’s no better way to do that than creating a brand new online course. The only thing you need is a course-creation platform to do that.
Thinkific is an intuitive and easy-to-use platform for all teachers to create beautiful online courses in no time. The platform adjusts easily to various teaching styles through the use of multimedia materials, from presentations to videos to quizzes to member communities.
Best of all, no coding skills are required. Just pick a gorgeous template and quickly customize it to your need with a drag-and-drop editor.
Get started today for free and see how easy creating an effective course can be.
This was originally published in June 2022, it has since been updated in February 2024 to include new info.